How to Choose the Best Casters for Heavy-Duty Equipment
When it comes to moving heavy machinery, carts, containers, or industrial equipment, selecting the right heavy-duty casters is crucial. The correct caster choice ensures safety, reduces downtime, and prolongs equipment life. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key considerations to choose the optimal casters for heavy-duty use.
What Are Heavy-Duty Casters?
Heavy-Duty casters are specialized wheels and mounting units built to support substantial loads—often ranging from 1,000 up to several thousand pounds per caster. Unlike standard casters, they use reinforced materials such as steel, cast iron, or heavy polyurethane, and typically have larger diameters, thicker treads, strong bearings, and robust mounting assemblies.
You’ll find heavy-duty casters in settings like manufacturing plants, automotive production, industrial handling, and anywhere large equipment must be mobile yet stable.
5 Critical Factors in Choosing Heavy-Duty Casters
To pick the best heavy-duty casters for your application, evaluate the following:
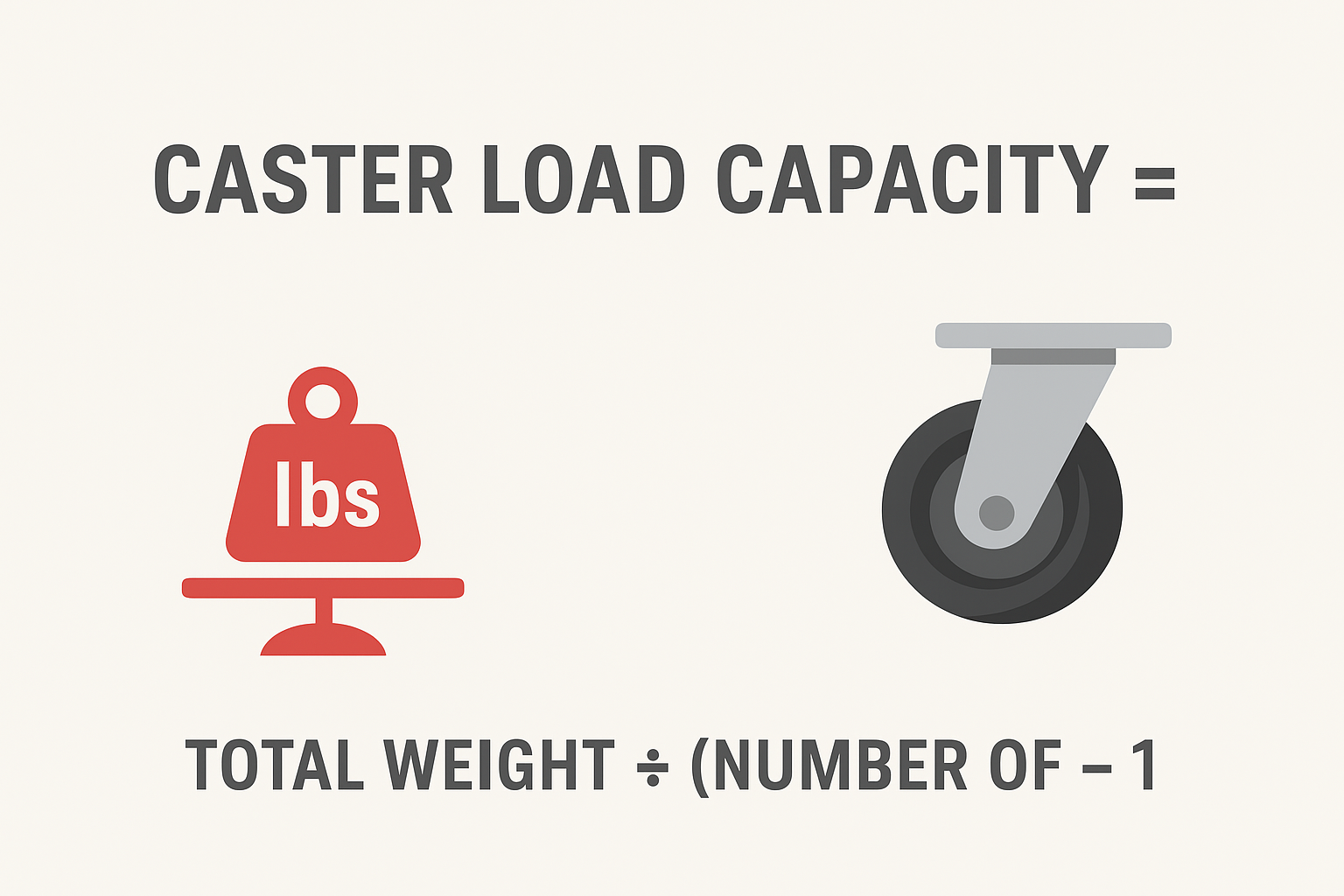
1. Load Capacity (Safe Working Load)
First, determine the total weight of your equipment plus any additional load it may carry (e.g. inventory, tools, materials).
Divide that total among the number of casters you’ll use (often total weight ÷ (number of casters – 1) to allow for uneven loading).
Always select casters whose load rating exceeds your calculated requirement. Overloading a caster leads to wobble, failure, and unsafe conditions.
2. Wheel Tread Material & Construction
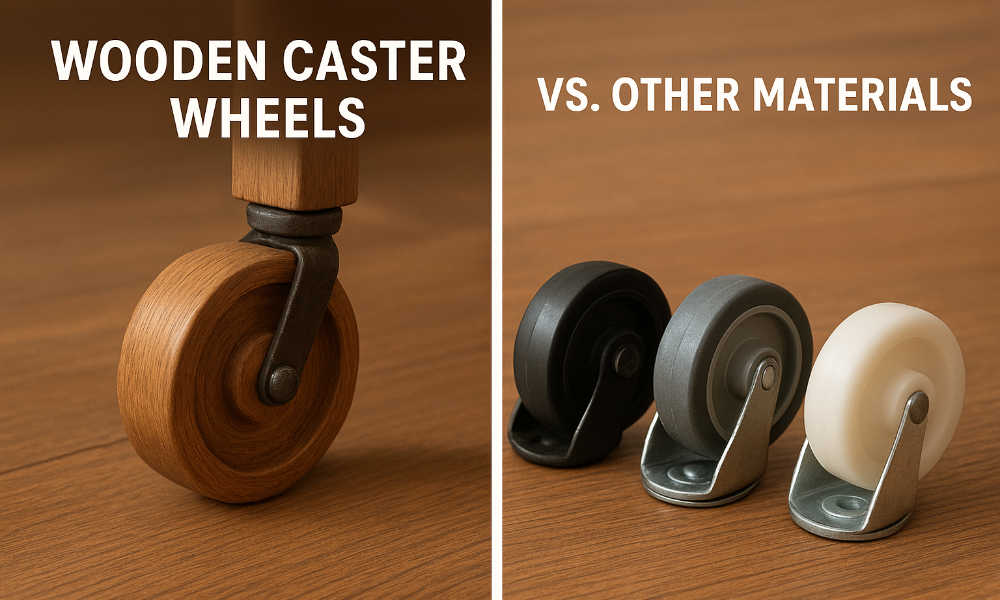
The wheel’s material directly affects performance, durability, noise, and floor protection. Common options include:
- Polyurethane: Excellent general-purpose choice. It resists chemicals, rolls smoothly on hard floors, and offers moderate load capacity.
- Steel / Cast Iron: Ideal when extreme loads or rough surfaces are involved. Very strong but may be noisy and less forgiving on the floor.
- Rubber / Elastomeric: Offers cushioning and vibration isolation, but may not be suitable for the highest loads or harsh conditions.
- Nylon, Phenolic, or Composite: Lightweight but strong; good in some cleanroom or chemical environments.
Match the wheel material to your facility floor type, obstacles, and operational environment.
3. Wheel Diameter & Width
Larger wheels roll over cracks, thresholds, and debris more easily and reduce rolling resistance.
However, larger wheels may require more vertical clearance or reduce stability if the center of mass shifts.
Width matters too—wider wheels distribute load better and reduce pressure on the floor.
Balance wheel size with your space constraints, floor condition, and load requirements.
4. Environmental Conditions & Special Requirements
Your operating environment has a big impact:
- High temperatures (e.g. ovens, foundries) demand heat-rated wheels and bearings.
- Chemical exposure, moisture, or corrosive agents call for casters with corrosion-resistant materials (stainless steel, plated finishes, special seals).
- Cleanrooms, hospitals, and food areas may require non-marking, low-outgassing, and easy-to-clean wheel surfaces.
- Outdoor or rough terrain environments benefit from casters with rugged treads and sealed bearings.
Choosing a caster suited to your environment prevents premature wear, corrosion, or failure.
5. Maneuverability, Steering & Ergonomics
Use swivel casters (able to rotate 360°) for better maneuverability in tight spaces.
Combine swivel and rigid (fixed) casters to control straight-line travel while maintaining steering options.
Consider locking casters (with brakes) to secure equipment in place when stationary.
Also assess push/pull force and ergonomics: well-designed casters reduce strain on operators.
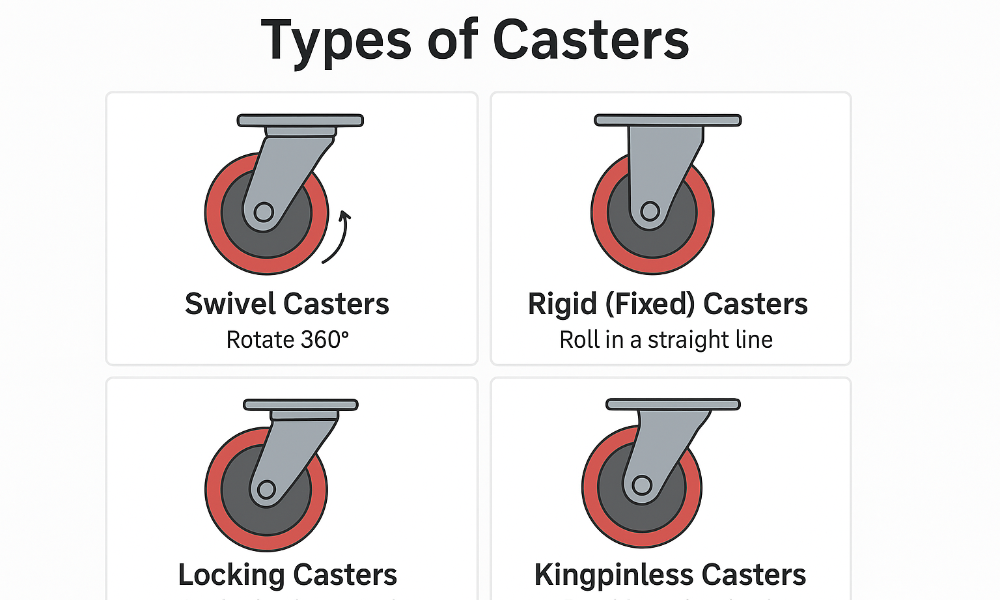
Types of Heavy-Duty Casters & Their Uses
Different forms of heavy-duty casters cater to varied scenarios:
- Swivel Casters: Rotate fully; ideal for carts, dollies, and equipment needing directional changes.
- Rigid (Fixed) Casters: Do not swivel; excellent for straight-line stability, often paired with swivel units.
- Locking Casters / Brakes: Prevent rolling or swiveling when engaged—vital for safety on inclines or when equipment must stay put.
- Dual-Wheel Casters: Two wheels in one frame help spread load and reduce floor pressure; often used in very heavy or high-stress applications.
- Kingpinless / Maintenance-Free Designs: These reduce the number of moving parts and maintenance needs, enhancing reliability.
Matching Casters to Specific Work Environments
Here are suggestions by environment:
Environment / Use Case |
Recommended Features |
Notes |
|
Manufacturing Plant |
Polyurethane or steel wheels with heavy load rating | Able to withstand heavy loads and rough floors |
|
Cleanrooms / Medical |
Non-marking, chemical-resistant wheels & stainless hardware | Prevent contamination and corrosion |
| Outdoor & Rough Terrain | Corrosion-resistant casters, rugged tread |
Handle wet and uneven surfaces |
| High-Heat Zones | Heat-resistant wheel compounds, sealed bearings |
Avoid melting or degradation |
Final Tips & Best Practices
Always overspec your caster load rating by a margin (typically 20–30%) for safety and longevity.
Ensure your mounting surface (plate, stem, bolt pattern) is rigid and compatible.
For large equipment, consider consultation with caster specialists to model dynamic loads, shock, and stress.
Regular inspection and maintenance (lubrication, bearing checks) extend the life of your casters.
Document usage, wear patterns, and replacement intervals to optimize uptime.
In summary, choosing the best heavy-duty casters for your equipment isn’t just about load capacity. It’s about matching load, materials, environment, maneuverability, and ergonomics. Investing in the right casters from the start saves you repair costs, reduces downtime, and keeps operations safer and smoother.
Get Your Custom heavy duty Casters Today
Contact us today to get samples, catalogs, or a custom quote.
Email: [sales02@targetcasters.com]
WeChat/WhatsApp Support Available:+86 189 5830 8581