Plain Bore vs Roller Bearings for Caster Wheels
Introduction
When selecting caster wheels for industrial or commercial applications, the bearing type is a critical design decision. Not all caster wheels are created equal—and the internal bearing configuration notably impacts performance, load capacity, durability, and maintenance.
This article explores the key differences between plain bore bearings and roller bearings, explains what is a plain bore bearing, and offers guidance on choosing the right bearing type for your caster wheel application.
What is a plain bore bearing?
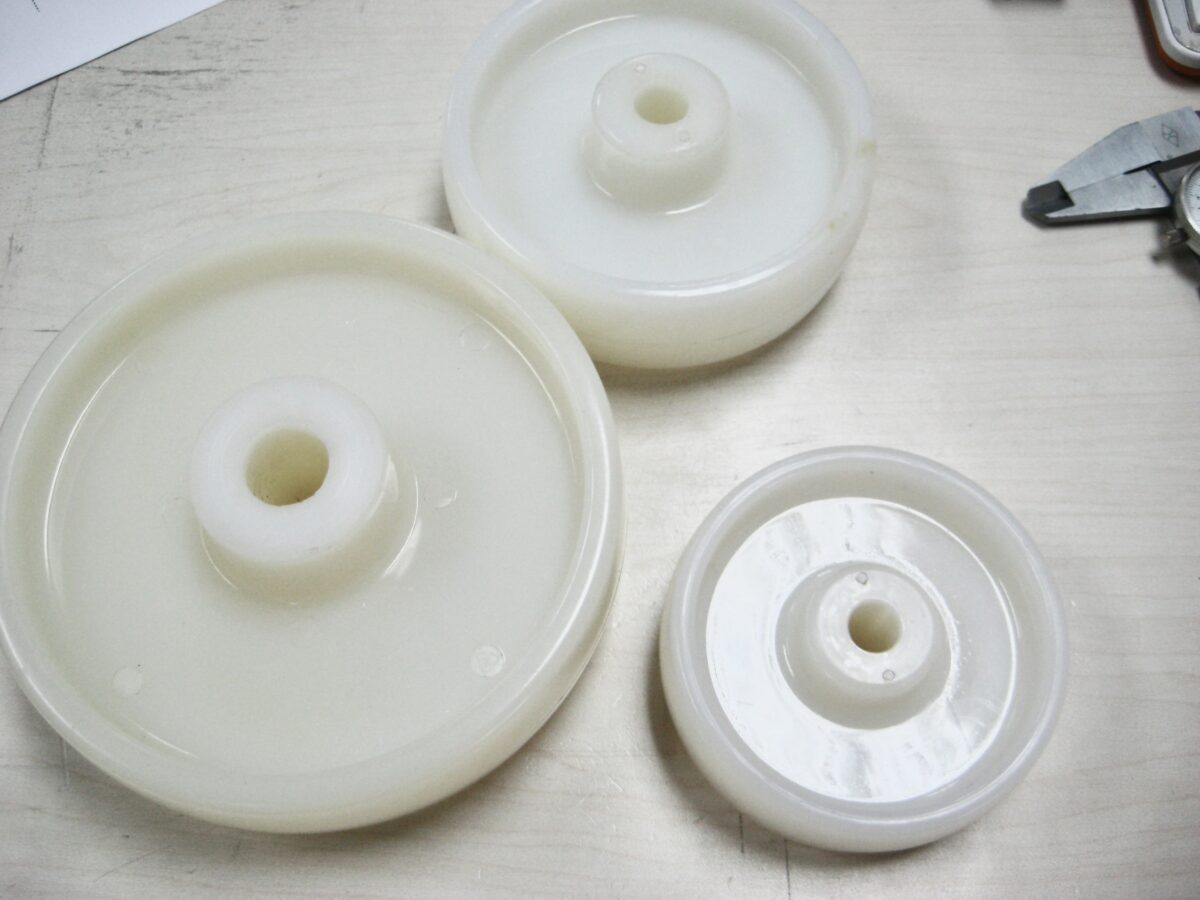
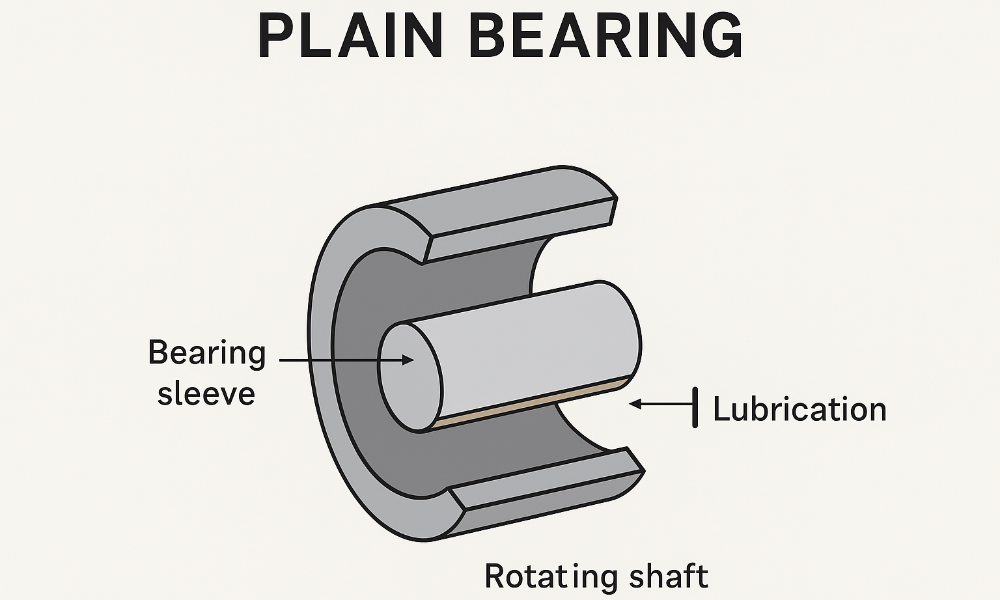
A plain bore bearing—also referred to as a sleeve bearing in the context of caster wheels—is one of the simplest bearing designs. The “bore” of the wheel is simply a smooth cylindrical hole in the wheel hub (or wheel centre) through which the axle passes. The wheel turns directly on the axle, or on a smooth bushing, without the use of rolling elements such as balls or rollers.
Key points about plain bore bearings:
- They rely on sliding contact between the bore/hub and the axle (or sleeve) rather than rolling.
- Because the design is simple (just a smooth bore, no cage or rollers), it tends to cost less and have fewer parts that can fail.
- They are often maintenance-free, or at least very low maintenance, since there are no rolling elements to clean or replace (though lubrication may still benefit the sliding interface).
- They are suitable for moderate loads and speeds, but their load capacity and efficiency tend to be lower compared to roller bearings because sliding friction is higher and contact stresses can be greater.
In the context of caster wheels, when you see “plain bore” it usually means the wheel hub has a bore sized to fit over the axle directly, and the hub material (or perhaps a bushing inside) provides the bearing surface.
What is a Roller Bearing?
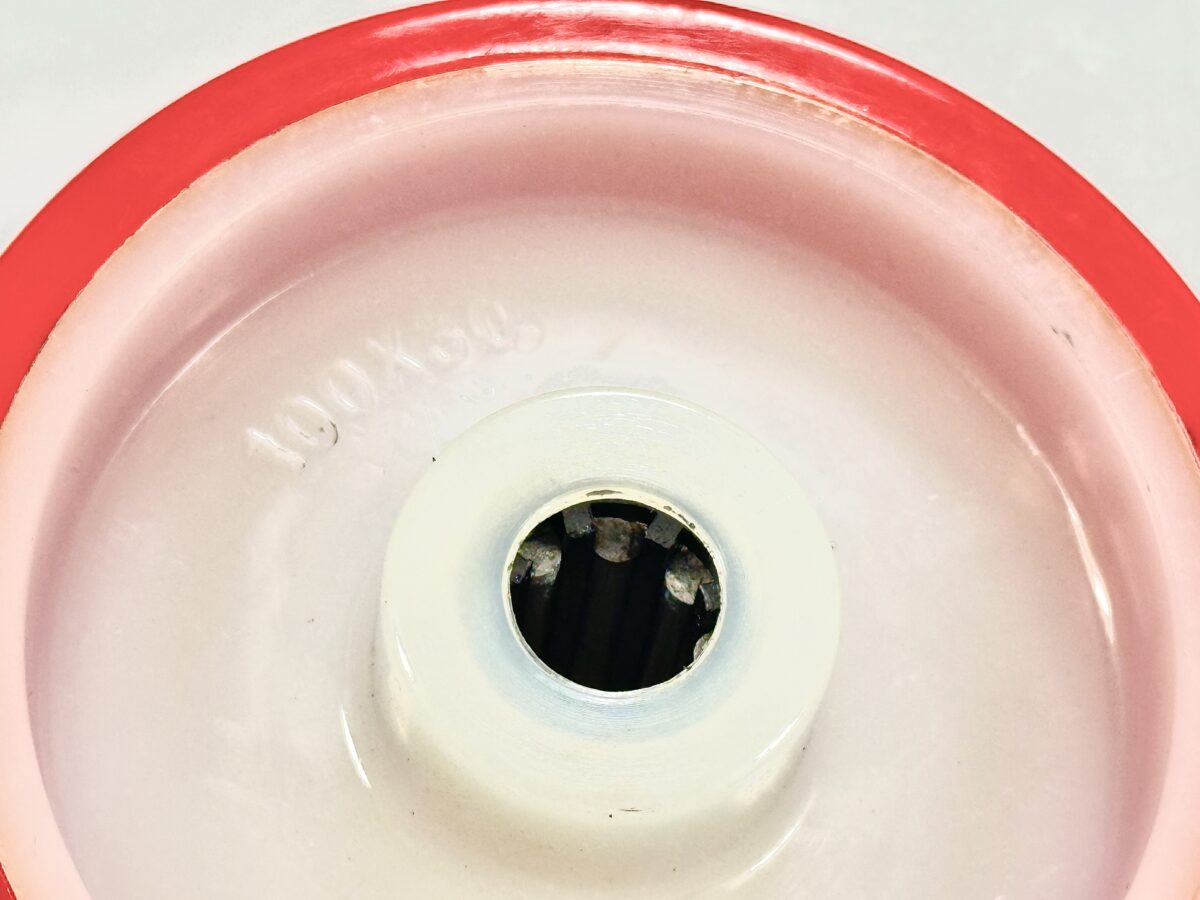
In contrast, a roller bearing for a caster wheel incorporates cylindrical rollers arranged between an inner and outer race (or hub-and-sleeve arrangement) and often a cage to keep the rollers spaced. As the wheel rotates, the rollers roll rather than slide, reducing friction and distributing load more evenly across contact surfaces. The general features of roller bearings include:
- Rolling elements (cylindrical rollers) that reduce friction compared to plain sliding contact.
- A race or track in which the rollers run, enabling smoother rotation and often lower torque required to start turning.
- Lower heat generation and better performance under higher speeds and heavier loads (when properly specified).
- Potentially higher cost and more complex design than plain bore bearings.
- Might require lubrication or maintenance, depending on the configuration and environment.

Side-by-Side Comparison: Plain Bore vs Roller Bearings
Here is a detailed breakdown of how plain bore and roller bearings compare for caster wheel applications:
Feature |
Plain Bore Bearings |
Roller Bearings |
|
Design complexity |
Very simple: smooth bore on axle or sleeve. | More complex: cage, rollers, outer/inner race. |
| Load capacity | Moderate. Because of sliding contact and often single or limited contact points, loads can induce higher stresses. |
Higher. Rollers distribute loads across multiple linear contact points and spread stress, improving capacity. |
|
Friction / efficiency |
Higher friction due to sliding contact, which means more torque to start motion and possibly more wear. | Lower friction thanks to rolling contact; smoother operation and less energy required to move. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance – fewer parts, often no lubrication required (though some lubrication helps) since no rollers. |
Maintenance may be higher: need to maintain lubrication, watch for wear of rollers/cages, ensure proper sealing especially in dirty environments. |
|
Durability in harsh environments |
Good if simple and robust; fewer parts to fail. But sliding surfaces may wear faster under heavy or frequent dynamic loads. | Better suited for dynamic heavy loads but can be more vulnerable to contamination, misalignment, lack of lubrication, or shock loads if not properly protected. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost upfront because of simpler design. |
Typically higher cost due to more precision engineering and more components. |
|
Best use cases |
Light to moderate loads, simple duty cycles, cost-sensitive applications, low speed or infrequent motion, clean environments. |
Heavy-duty casters, frequent movement, higher speeds, larger loads, where smooth motion and longevity are critical. |
How to Choose Between the Two for Caster Wheels
When deciding between plain bore bearings and roller bearings for caster wheels, consider the following application factors:
Load (weight) and duty cycle
- If the caster will carry relatively modest loads and the movement is infrequent or slow, plain bore bearings are often adequate.
- If the caster will support heavy loads, repeated motion, or high speeds, roller bearings may be the better choice.
Motion type and speed
- For equipment that is stationary most of the time or only occasionally moved, plain bore may suffice.
- For carts, racks, conveyor supports or mobile equipment where wheels roll frequently or need to swivel smoothly, roller bearings improve performance.
Environment and maintenance capability
- In clean, controlled environments with minimal debris, a roller bearing might work beautifully.
- In dirty, dusty, or wet environments where contaminants might compromise roller cages or lubrication, a plain bore bearing may be more robust (given proper materials and bushings).
- Also consider how easy it is to service the bearing: if maintenance is difficult, simpler plain bore bearings may offer advantage.
Cost constraints
- Budget is always a factor: plain bore bearings are typically less expensive.
- But if the cost of downtime, replacement or failure is high, investing in roller bearings may pay off.
Expected lifespan and reliability
- If the caster wheel is critical to operations and replacement or failure is costly or disruptive, go with the more reliable configuration — often the roller bearing design.
- For less critical use, plain bore may be perfectly acceptable.
Space or design constraints
- Roller bearings may require slightly more space, more robust axles or hub designs. If space or mounting is constrained, plain bore may be simpler.
Practical Tips for Specification and Use
When specifying a plain bore bearing caster, check the axle fit, material of the bore (is it hardened steel, or is there a bushing or sleeve?), lubrication or self-lubricating options (e.g., bronze bushings).
For roller bearing casters, examine the bearing manufacturer’s load ratings, sealing against contaminants, lubrication intervals, and whether the rollers are hardened steel or stainless (for corrosive environments).
Consider whether the caster will swivel or just roll: if swiveling is involved, bearing type in the swivel head may differ and choose accordingly.
For retrofits or replacement of caster wheels, check the existing bearing type, axle size, hub width, and mounting plate or stem to ensure compatibility.
Monitor performance in service: if you observe high rolling resistance, noisy movement, or wear in a plain bore bearing caster, it may be time to upgrade to roller bearings. Conversely, if a roller bearing caster fails prematurely due to contamination or lack of lubrication, the plain bore alternative may have been more suitable.
Conclusion
In summary, the choice between plain bore bearings and roller bearings for caster wheels hinges on load, environment, cost, and expected performance. Plain bore bearings (simple sleeve-type designs) offer a cost-effective, low-maintenance solution for moderate duty applications, and by understanding what is a plain bore bearing you’ll see why the simplicity is appealing. Roller bearings, on the other hand, bring enhanced load capacity, smoother rolling, and better performance when the application demands it—but with higher cost and possibly more maintenance.
By carefully evaluating your application’s requirements—load size, duty cycle, environment, maintenance capability—you can make an informed decision and select the caster wheel bearing configuration that delivers reliable and cost-effective service.
If you’d like help selecting specific caster wheels or bearing types for your equipment, I’d be happy to assist!